Table of Contents
- Introduction to Point-of-Sale Terminals
- Evolution of POS Terminals
- Types of POS Systems
- Key Features of Modern POS Terminals
- Advantages of Implementing POS Terminals
- Security and Compliance in POS Systems
- POS Terminals and Business Analytics
- Future Trends in POS Technology
Today’s fast-paced retail environment demands that transaction processing be swift and reliable in order to remain profitable; that’s where Point-Of-Sale (POS) terminals play their part; these systems facilitate smooth exchanges of goods and services for money exchanged at the checkout process.
Introduction to Point-of-Sale Terminals

Point-of-Sale Terminal: What it is and How It Works
A Point-of-Sale terminal (POS terminal) is a hardware system used to process card payments at retail locations. This device reads customer payment cards (credit, debit or mobile wallet), verifies available funds in their accounts and then transfers funds between accounts – with records kept of every transaction completed successfully. Modern POS terminals are capable of processing different payment types including chip cards, magstripe cards and contactless payments via NFC-enabled digital wallets.
Importance of POS Terminals in Retail Operations
POS terminals are essential tools for retail transactions as they not only handle payments but also integrate with inventory management and sales reporting systems to provide insight into consumer behavior and business performance. Their integration allows retailers to better control their inventory levels, monitor sales trends and optimize business operations overall.
Evolution of POS Terminals
POS systems have grown alongside retail technology, from simple cash registers to sophisticated systems capable of much more than simply processing payments.
Initial Cash Registers
It all started with the invention of cash registers in the late 19th century, serving to secure and record sales transactions. Over time these mechanical devices evolved into electronic cash registers (ECRs) with enhanced functions like sales reporting and basic inventory tracking capabilities.
Introduction of Electronic Point-of-Sale Systems (POS) Systems
In the 1970s and 80s, electronic point of sale systems became common. These integrated software packages could manage inventory, sales data, customer information and customer interactions. Digital transactions also took off at this time with systems capable of taking credit card payments while producing digital receipts.
Emergence of Mobile and Cloud-Based POS Systems
In the late 2000s and early 2010s, there was a revolution brought on by mobile POS (mPOS) systems and cloud-based POS systems. These innovations allowed businesses to process transactions on portable devices stored in the cloud with flexible scalability options; retailers could access real-time information anywhere at any time to facilitate better decision-making while improving customer experiences.
Types of POS Systems
Modern POS systems come in various forms to accommodate for the specific requirements of different business types.
Traditional Countertop POS
Traditional countertop POS systems are among the most frequently used systems, consisting of a central terminal connected to peripheral devices like barcode scanners, receipt printers and card readers. These systems tend to be utilized in brick-and-mortar stores where there is a dedicated checkout counter.
Mobile POS (mPOS)
Mobile Point-of-Sale (mPOS) systems are flexible POS solutions designed for businesses that need flexibility, such as restaurants, pop-up shops and service providers with limited space. These portable mPOS solutions support contactless payments and make for ideal environments where space may be an issue.
Self-Service Kiosks
Self-service kiosks have become an increasingly popular feature in fast food restaurants and retail stores, enabling customers to process transactions independently – decreasing wait times while providing enhanced customer experiences. Many come equipped with touchscreen interfaces and support various payment methods.
Cloud-Based POS
Cloud-based POS systems leverage the internet’s vast power for real-time data access, seamless updates, and remote management capabilities. These solutions are especially suitable for businesses with multiple locations since they enable centralized control and uniform data across each outlet.
Industry-Specific POS Systems
Some POS systems are tailored specifically for various industries, such as restaurant POS with features like table management and split billing capabilities, or retail POS that offers advanced inventory tracking and customer relationship management (CRM) features.
Key Features of Modern POS Terminals
Modern POS terminals come packed with features designed to simplify business operations and enhance customer experiences.
Payment Processing
At the core of any POS terminal lies its ability to process payments efficiently and securely – including various payment methods such as:
- Chip Cards: EMV technology ensures secure transactions by encrypting card data.
- Magstripe Cards: Traditional method for swiping cards is still widely used today.
- Contactless Payments: NFC technology facilitates quick and secure mobile wallet payments such as Apple Pay and Google Wallet for swift payments on the go.
Modern POS systems come equipped with inventory management features to assist businesses in keeping an accurate record of inventory data, thus decreasing chances of stockouts or overstocking.
Reporting and Analytic Services for Sales Personnel.
Comprehensive sales reporting features enable businesses to assess performance metrics, track sales trends and make data-driven decisions. Reports may include specific details regarding product sales by product type, time period or employee to help optimize operations and ensure business efficiency.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
POS systems equipped with CRM features enable businesses to efficiently maintain customer information, purchase history and preferences – invaluable data that can be leveraged to personalize marketing initiatives, implement loyalty programs and boost customer satisfaction.
Employee Management POS systems with employee management features allow businesses to track working hours, manage schedules, and assess sales performance of individual staff members – an essential step in optimizing workforce efficiency and lowering labor costs.
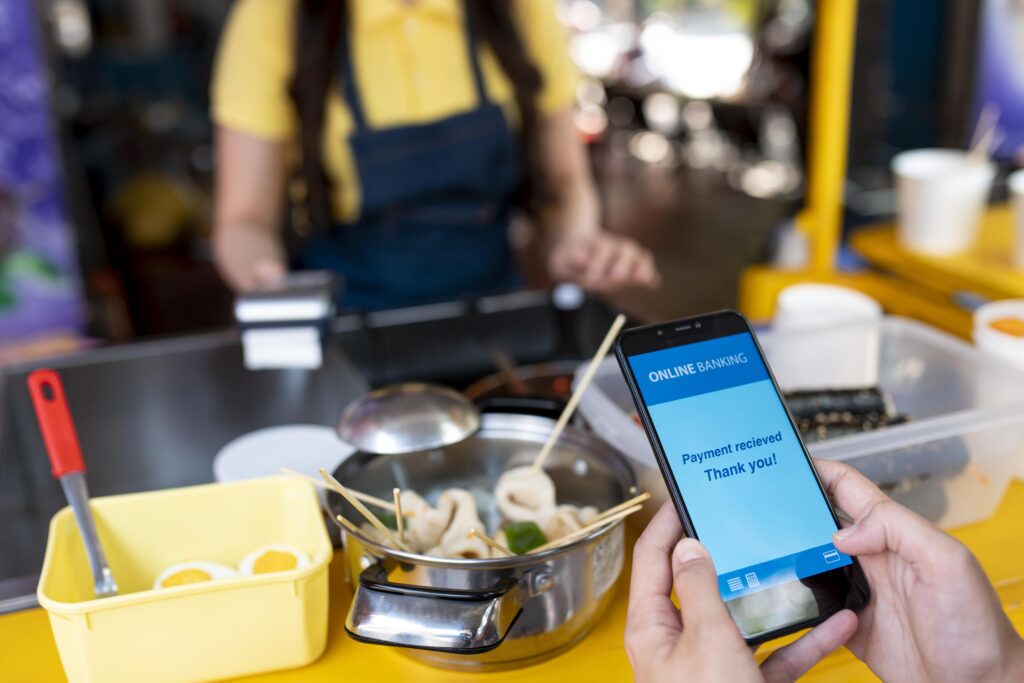

Advantages of Implementing POS Terminals
Implementing point of sale terminals offers many advantages that can drastically increase business operations and customer satisfaction.
Acceleration and Accuracy Enhance Transaction Performance.
POS terminals simplify the checkout process, decreasing wait times and errors during transactions to provide customers with an improved shopping experience. As a result, customer satisfaction increases and satisfaction scores rise accordingly.
Modern POS systems employ robust data security measures such as end-to-end encryption and tokenization to protect sensitive payment data, helping prevent fraud while guaranteeing secure transactions.
Better Inventory Control strategies
Businesses leveraging inventory management features can maintain accurate stock levels, reduce wastage and ensure popular products remain readily available, ultimately leading to greater control and increased profitability.
Real-Time Data and Insights from Our Real-Time Analytics Solutions Provide Real-time insights for better decision making
Cloud-based POS systems give businesses real-time access to sales and inventory data, enabling them to make informed decisions quickly. This enables businesses to identify trends quickly, adjust strategies accordingly, and remain competitive in the market.
Improve Sales and Improve Customer Satisfaction
Effective POS systems can enrich the shopping experience for customers by shortening checkout times, offering various payment options, and personalizing interactions – leading to higher customer loyalty and sales growth.
Security and Compliance in POS Systems
Security should always be an essential consideration when it comes to any POS system, due to the sensitive payment data involved.
Data Protection and Encryption Solutions
POS systems must adhere to industry standards such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), which outlines measures for protecting cardholder data. Cryptography and tokenization are often employed to safeguard transaction data.
Fraud Prevention EMV technology, which employs chip cards for transactions, helps reduce card-present fraud. Furthermore, NFC payments add another layer of protection by eliminating physical contact between terminal and customer.
Compliance with Regulations
Businesses must ensure their POS systems comply with local and international regulations regarding data protection and electronic payments, adhering to standards set by payment card networks or government bodies.
POS Terminals and Business Analytics
Integrating point of sale systems and business analytics tools offers invaluable insights that can fuel both growth and efficiency.
Sales Analytics
POS systems generate detailed sales reports that enable businesses to understand which products are performing well, when peak sales times occur and evaluate promotional initiatives effectively.
Customer Behavior Insights
Analysis of customer data collected via POS systems allows businesses to gain insight into purchasing patterns, preferences and trends of customers. With this insight comes an opportunity for tailoring marketing strategies and increasing customer engagement.
Tracking Operational Efficiency
By keeping an eye on metrics like transaction times, inventory levels and employee performance data, businesses can identify areas for improvement and create strategies to enhance operational efficiency.
Future Trends in POS Technology
The Point-of-Sale industry is continually changing, as new technologies and trends impacting retail transactions are introduced into the mix.
Mobile and Contactless Payments
Mobile and contactless transactions are expected to become increasingly popular due to consumer demand for convenience and security, making businesses aware of this payment method imperative for success. Businesses should ensure their POS systems can accommodate these payment methods for maximum effectiveness.
AI and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) technologies are being integrated into POS systems to deliver predictive analytics, personalized customer experiences, and enhanced fraud detection capabilities.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain Technology Blockchain has the potential to revolutionize payment processing by providing a decentralized, secure, and transparent way to conduct transactions. POS systems may integrate blockchain networks to achieve these benefits.
Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT devices can enhance POS systems’ functionality by providing real-time inventory tracking, automated restocking, and increased customer interactions through connected devices.
Conclusion
Point-of-Sale (POS) terminals are essential tools for modern retail transactions, providing businesses with features to improve efficiency, security, and customer satisfaction. By understanding the evolution, types, features, and advantages of POS systems businesses can make informed decisions regarding implementation and optimization processes – staying current with industry trends ensures businesses remain competitive and capable of meeting customers’ evolving needs.
Evolution of POS Terminals
Point-of-Sale (POS) terminals reflect the technological advancements that have revolutionized retailing over the past century. From basic cash registers to complex cloud-based systems used today, their journey is an impressive story of innovation and adaptation.
Early Cash Registers
POS terminals can be traced back to Ohio saloon owner James Ritty’s invention of the cash register during the late 19th century, known as Ritty’s Incorruptible Cashier. This mechanical device was intended to deter employee theft while recording accurate transactions; later known as modern POS systems.
Key Features:
Key Features of ECRs (Electronic Cash Registers): These features include mechanical operation, secure cash storage and basic sales recording.
Electronic Cash Registers (ECRs)
Electronic cash registers (ECRs), introduced in the mid-20th century, marked another monumental leap forward by including electronic components for performing calculations and storing transaction data – this marked digital transaction processing and provided businesses with more accurate and efficient ways to manage sales transactions.
Key Features of Electronic Point-Of-Sale Systems (ePOS Systems) include electronic transaction recording and basic inventory tracking for greater accuracy and efficiency, plus introduction of E-POS Systems for use at point of sale (POS).
Introduction of Electronic POS Systems
In the 1970s and 80s, electronic point of sale systems integrating software and hardware were introduced. These advanced POS systems could manage credit card payments, generate digital receipts and produce detailed sales reports; their integrated payment processing capabilities allowed businesses to accept various payment types including credit and debit cards.
Key Features:
Key Features of Inventory and Sales Management Software:
- Integrated software for inventory and sales management
- Support for credit card payments
- Generating digital receipts Emergence of Mobile and Cfloud-Based POS Systems (Point of Sales Systems).
Emergence of Mobile and Cloud-Based POS Systems
In the late 2000s and early 2010s, businesses experienced a dramatic transformation with the rise of mobile point of sale (mPOS) systems and cloud-based POS solutions. These innovations revolutionized how transactions were processed within businesses by providing unparalleled flexibility and scalability.
Mobile POS (mPOS): Mobile POS enabled businesses to process transactions using portable devices like smartphones and tablets – an especially advantageous solution for restaurants, pop-up shops, and service providers that needed mobility.
Key Features:
- Portability and flexibility
- Support for contactless payments
- Integration with mobile wallets
Cloud-Based POS Systems: Utilizing the power of the internet, cloud-based POS systems used the cloud-computing model to store data and process transactions real time. This enabled businesses with multiple locations to maintain central control and consistent information across all locations; furthermore, remote management and real time analytics was also possible with cloud systems.
Key Features:
Key Features of Real-time Data Access and Analysis for Multiple Locations in Real Time (RiLDA/RMTR) POS Systems / Industry-Specific POS Solutions (ISPOSs).
Industry-Specific POS Systems
As POS technology developed, industry-specific solutions started to emerge. These systems were tailored specifically to the unique requirements of different sectors such as retail, hospitality and healthcare – for instance restaurant POS systems featured features like table management and split billing while retail POS offered advanced inventory tracking and customer relationship management (CRM) capabilities.
Here are a few examples of industry-specific POS Systems:
Restaurant POS systems typically include table management, split billing and kitchen display systems as key functions of table service; retail POS includes advanced inventory tracking capabilities with CRM integration for loyalty programs; healthcare POS applications typically involve patient billing, insurance claim processing and appointment scheduling functions.
Summary The progression of point of sale terminals from mechanical cash registers to advanced cloud-based systems showcases retail technology’s advancement. Each stage brought new features that enhanced transaction processing, inventory management, and overall business operations. As these POS systems continue to develop, businesses must adapt accordingly in order to remain competitive while meeting customers’ changing demands.

Importance of POS Terminals in Modern Retail
POS terminals have become an essential tool in modern retail, revolutionizing how businesses interact with customers and streamline transactions. They play a critical role in streamlining transactions, improving customer experiences and offering valuable insight into business operations – here we explore their multiple functions in today’s retail landscape.
Streamlined Transactions
One of the primary purposes of POS terminals is to facilitate fast and secure transactions, using various payment methods like credit/debit cards, mobile payments and contactless payments to ensure seamless and secure payment processing – this helps reduce wait times while improving customer experience overall.
Key Benefits of POS Terminals:
- Speed and Efficiency: POS terminals facilitate quick transactions that reduce queues while improving customer satisfaction.
- Multiple Payment Methods: Offering various payment methods allows POS terminals to cater to various customer preferences.
- Accuracy: Automated calculations reduce human error, creating more accurate transaction records and providing enhanced customer experiences. amelioration
POS terminals significantly enhance customer experiences by offering convenience and personalized services. Modern POS systems store customer data, track purchase histories and manage loyalty programs in order to create tailored promotions and rewards that foster customer retention and foster repeat business. Such personalized offerings build customer loyalty while encouraging repeat business.
Key Benefits:
- Loyalty Programs: Utilization of loyalty programs allows businesses to recognize loyal customers with discounts, points or special offers.
- Customer Data Management: Storing and analyzing customer information helps businesses understand purchasing behavior and preferences more thoroughly.
- Digital Receipts: Offering digital receipts via email or SMS allows businesses to reduce paper waste while giving customers easy access to their purchase records.
- Effective Inventory Management:Retail businesses rely on efficient inventory management practices to ensure they always have enough of their desired products in stock at any given moment.
POS terminals equipped with advanced inventory tracking capabilities allow businesses to monitor stock levels live, automate reordering processes, and avoid overstocking or stockouts.
Key Benefits of Real-Time Tracking:
- Real-time tracking provides accurate and up-to-date stock levels at all locations.
- Automated Reordering: When inventory levels fall below predefined thresholds, POS systems can generate purchase orders automatically through their system.
- Detail Reporting: Receive detailed reports on inventory turnover, shrinkage and profitability.
POS terminals have become indispensable tools in modern retail, revolutionizing the way businesses operate and interact with customers. They play a crucial role in streamlining transactions, enhancing customer experiences, and providing valuable insights into business operations. Here, we explore the multifaceted importance of POS terminals in today’s retail landscape.
Inventory Management
Effective inventory management is essential to retail businesses’ operations. POS terminals equipped with advanced inventory tracking capabilities enable retailers to monitor stock levels in real time, automate reordering processes, and reduce instances of overstocking or stockouts.
Key Benefits:
- Real-Time Tracking: Provide accurate, up-to-the-minute stock levels across all locations.
- Automated Reordering: POS systems can automatically generate purchase orders when inventory drops below a predefined threshold.
- Detailed Reporting: Offering extensive reports on inventory turnover, shrinkage and profitability is crucial to business.
| Inventory Management Features | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Real-Time Tracking | Up-to-date stock information |
| Automated Reordering | Prevents stockouts and overstock |
| Detailed Reporting | Insights into inventory turnover |
Sales and Business Analytics
Modern POS systems come equipped with robust analytics tools that offer valuable insight into sales performance, customer behavior and overall business operations. By analyzing transaction data, businesses can identify trends, evaluate marketing campaigns’ effectiveness and make data-driven decisions to streamline operations and enhance productivity.
Key Insights:
- Sales Trends: Analyzing sales data helps identify best-selling products and peak shopping times, while customer behavior analysis allows personalized marketing strategies.
- Operational Efficiency: Increased insights into employee performance, transaction times and inventory management can boost operational efficiency.
Case Study: A clothing retail store implemented a cloud-based POS system to analyze sales data across its multiple locations. Their insights revealed that certain products were consistently selling out while remaining overstocked elsewhere; by reallocating inventory based on these insights, the store optimized stock levels, reduced excess inventory levels, and ultimately increased overall sales by 15%.
Security and Fraud Prevention measures
Security is a paramount concern in retail transactions. POS terminals play a critical role in ensuring secure transactions and protecting sensitive customer data. Modern POS systems incorporate advanced security features such as end-to-end encryption, EMV (Europay, Mastercard, and Visa) technology, and PCI-DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) compliance.
Key Security Features:
- End-to-End Encryption: Encrypting data from its point of entry all the way through to its final destination for secure transactions.
- EMV Technology: Helps combat counterfeit card fraud using chip card technology, providing additional layers of protection.
- PCI-DSS Compliance: Our payment processing and data protection solutions adhere to industry standards for secure payment processing and protection.
Quote: “Implementing a robust POS system with advanced security features is crucial for protecting both your business and your customers from fraud and data breaches.” – John Smith, Cybersecurity Expert
Integrate Other Business Systems.
POS terminals are not standalone devices; they must integrate seamlessly with other business systems like accounting software, Customer Relationship Management systems and eCommerce platforms for maximum efficiency and reduce manual data entry errors. By doing so, integration ensures an easy user experience.
Key Integrations:
- Accounting Software: Automated synchronization of sales data with accounting systems for accurate financial reporting.
- CRM Systems: Automated synching of sales data with accounting systems provides accurate financial reporting.
- E-commerce Platforms: Unified inventory and sales management across both online and physical stores allows for seamless operation.
Benefits of Integration:
- Reduced Manual Entry: Automated data synchronization saves time and errors while improving accuracy across business systems.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Simplified operations and resource optimization.

Types of POS Terminals and Their Features
POS terminals come in various types to meet various business needs and environments. Learning more about each type can help businesses choose an appropriate POS terminal system; here we discuss some of the primary types and their key features.
Countertop POS Terminals
Countertop POS terminals are one of the oldest and most widely utilized forms of point of sale (POS) systems, commonly found in retail stores, restaurants, and other fixed locations where transactions take place at designated checkout counters.
Key Features:
- Robust Hardware: Our solutions feature robust components such as barcode scanners, receipt printers and cash drawers that can withstand even the harshest environments.
- Comprehensive Functionality: Our payment services support various payment methods such as chip cards, magstripe cards and contactless payments – giving our users access to an array of payment solutions.
- Network Connectivity: Connect the device directly to the internet using Ethernet or Wi-Fi for seamless transaction processing and data synchronization.
Example: In general, retail stores use countertop POS terminals equipped with barcode scanners and receipt printers for quick product scanning, paper receipt printing capabilities and cash drawers for handling cash transactions. Furthermore, this system connects directly with their inventory management software for real-time updates on stock levels.
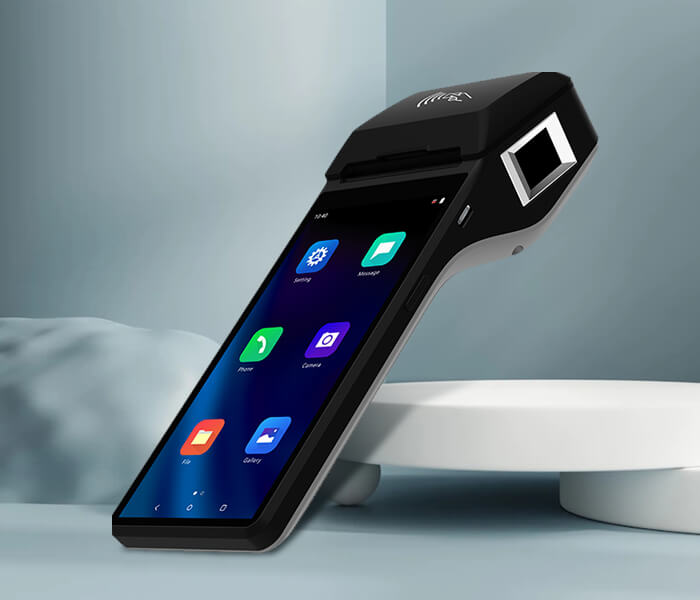
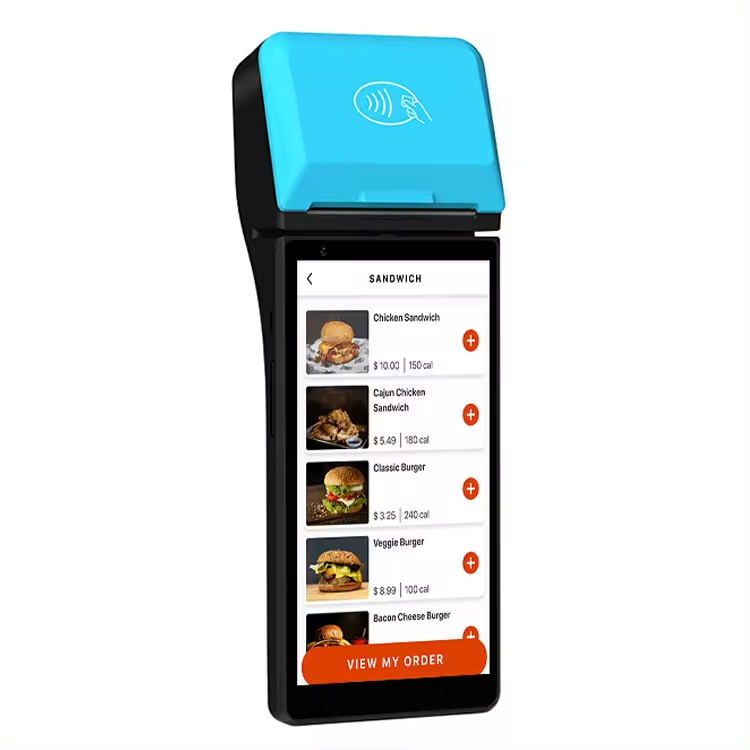
Mobile POS Terminals
Mobile POS (mPOS) terminals are portable systems designed to facilitate transactions in any part of a store or even on-the-go, making them especially beneficial for businesses requiring mobility such as food trucks, market stalls and pop-up shops.
Key Features:
- Portability: With its compact and lightweight design, this device allows for easy transport and use in various locations.
- Wireless Connectivity: Operating over Wi-Fi or cellular networks enables remote payment processing capabilities.
- Versatility: Can be easily integrated with smartphones or tablets for cost-effective solutions for small businesses.
Case Study: A food truck business adopted an mPOS solution to accept card payments at various locations. Utilizing a tablet connected to a card reader, they were able to process transactions quickly and efficiently – increasing sales by 20% due to offering customers cashless payment convenience.
| Mobile POS Features | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Portability | Flexibility to process payments anywhere |
| Wireless Connectivity | Operates over Wi-Fi or networks |
| Versatility | Cost-effective solution for small businesses |
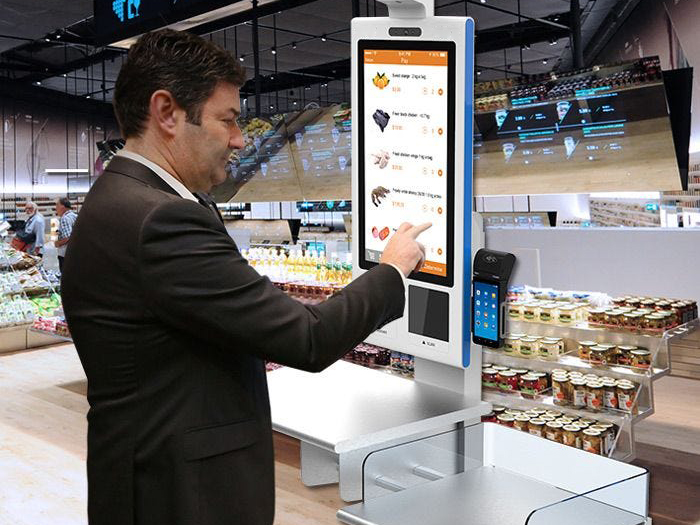
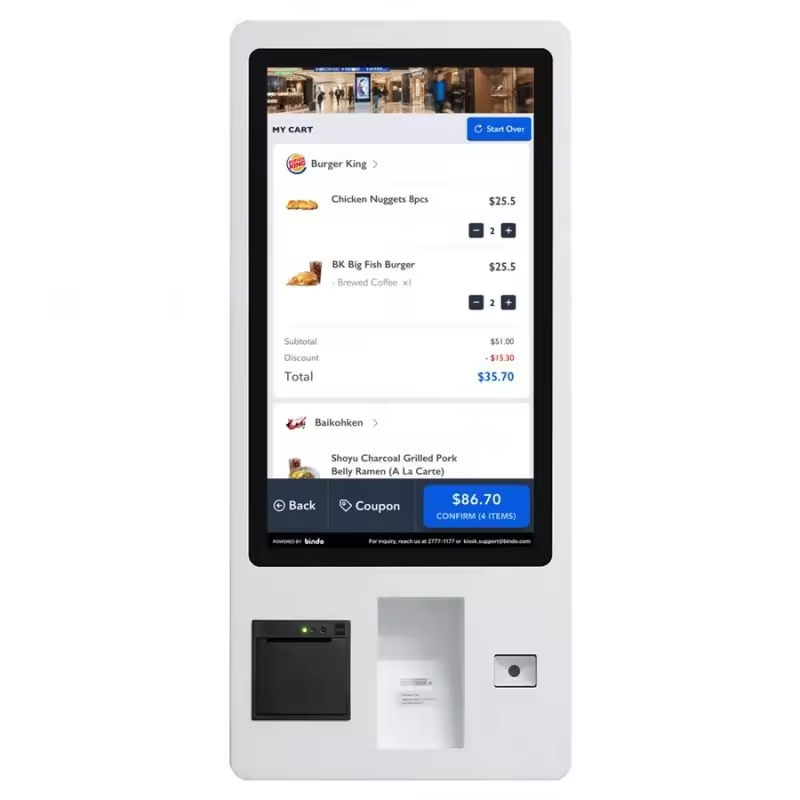
Self-Service Kiosks
Self-service kiosks have become an increasingly common sight in fast-food restaurants, cinemas and retail stores alike. These terminals allow customers to independently browse products, place orders and make payments without direct interaction from staff members.
Key Features:
- Touchscreen Interface: For simple navigation and order placement. experience
- Customization: Providing customers the ability to personalize their order for an enhanced shopping
- Efficient Transactions: Reduce wait times while relieving staff pressure during peak hours.
Example: A fast-food restaurant implemented self-service kiosks to streamline their ordering process and allow customers to place orders directly at kiosks, customize meals as desired and pay with various payment methods – this significantly decreased queues at the counter while freeing staff up for more efficient food preparation, further increasing efficiency overall.
Cloud-Based POS Systems
Cloud-based POS systems utilize cloud computing technology to store and manage data online, offering many advantages in terms of accessibility, scalability and data security. These solutions are ideal for businesses that require flexibility as well as integration with other digital tools.
Key Features:
- Remote Access: Business owners can quickly and securely access real-time data and reports from any internet connected device, anywhere in the world.
- Scalability: Our solution can easily adapt to accommodate business expansion and additional locations while our data security features ensure protection of customer and transactional information.
Benefits of Cloud-Based POS:
- Cost-Effective: Reduces the need for extensive on-premise hardware.
- Automatic Updates: Regular updates and maintenance are handled by the service provider.
- Integration Capabilities: Seamlessly integrates with e-commerce platforms, accounting software, and other business tools.
Quote: “Adopting a cloud-based POS system has completely revolutionized our business operations, providing real-time insight and the freedom to remotely manage our stores.” – Sarah Lee, Retail Business Owner
Integrated POS Systems
Integrated Point-of-Sale systems combine hardware and software components into one streamlined solution for comprehensive functionality, including payment processing, inventory control, customer relationship management (CRM), customer management (CRM), etc.
Key Features:
- All-in-One Solution: Streamlining processes and eliminating multiple standalone systems is crucial.
- Seamless Integration: Maintain a seamless data flow among business operations.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Streamlining processes and decreasing the need for multiple standalone systems is one way of streamlining operations and saving costs.
Example: One boutique clothing store deployed an integrated POS system for inventory, customer data tracking, and sales reporting. This seamless integration enabled more effective stock level management; tailored marketing campaigns to customer preferences; and detailed sales reports to aid with decision making.
Comparison of POS Terminal Types
| Type | Key Features | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Countertop POS | Robust hardware, comprehensive functionality | Retail stores, restaurants |
| Mobile POS | Portability, wireless connectivity, versatility | Food trucks, market stalls, pop-up shops |
| Self-Service Kiosks | Touchscreen interface, customization, efficient transactions | Fast-food restaurants, cinemas, retail stores |
| Cloud-Based POS | Remote access, scalability, data security | Businesses requiring flexibility and integration |
| Integrated POS | All-in-one solution, seamless integration, enhanced efficiency | Boutique stores, businesses with multiple operations |
Choosing the Right POS Terminal for Your Business
Selecting the right POS terminal for your business involves taking several factors into consideration, including its nature and volume of transactions as well as operational needs. This section will walk you through these key factors so you can make an informed decision.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a POS Terminal
- Business Type and Size
- Retail Stores: Retail Stores require robust systems with inventory management and customer relationship management (CRM) capabilities;
- Restaurants: Restaurants require features like table management, customization of orders, and split payments for payment processing.
- Mobile Businesses: Advantage of portable, mPOS systems for on-the-go transactions.
- Service-Based Businesses: Appointment scheduling and billing functionalities may be needed.
- Transaction Volume
- Transaction Volume Businesses with high transaction volumes need reliable and fast systems that can manage multiple transactions at the same time without incurring downtime, while low volume operations might prioritize cost-cutting solutions with limited functionality.
- Integration Needs
- Before purchasing a POS system, ensure it integrates smoothly with existing software such as accounting, payroll and e-commerce platforms. Also take into consideration any future integration needs as your business expands.
- Payment Methods
- Aim for a POS terminal that supports multiple payment methods, including chip cards, magstripe cards, contactless payments, mobile wallets and NFC authentication technologies.
- Budget
- Be mindful of both upfront costs and ongoing expenses such as hardware, software, transaction fees and maintenance when creating your budget. Examine the total cost of ownership to ensure it fits within your means.
- Security Features
- Select systems equipped with strong security measures to safeguard against data breaches and fraud. Features such as end-to-end encryption, tokenization and compliance with industry standards (e.g. PCI DSS) should all play a part. When Comparing Popular POS Systems.
Comparing Popular POS Systems
Here’s a comparison of some popular POS systems to help you make an informed choice:
| Feature | Square POS | Shopify POS | Clover POS | Lightspeed POS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Business Type | Retail, F&B, Service | Retail, e-commerce | Retail, F&B | Retail, e-commerce |
| Hardware Options | mPOS, countertop | mPOS, countertop | mPOS, countertop | mPOS, countertop |
| Integration | High | High | Medium | High |
| Payment Methods | All major types | All major types | All major types | All major types |
| Security Features | High | High | High | High |
| Cost | Low to medium | Medium to high | Medium to high | Medium to high |
| Scalability | High | High | High | High |
| Customer Support | Excellent | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
Case Study: As their business grew, a boutique switched from Square POS due to its low initial cost and ease of use to Shopify POS which provided seamless integration with their e-commerce platform and enhanced analytics capabilities.
Steps to Implement a POS System
- Assess Your Needs
- Assess Your Needs First, identify specific business requirements and desired features for a POS system. And be mindful of what transactions your business processes as well as the total volume.
- Research and Compare
- Research different point of sale systems and compare features, costs and customer reviews before selecting one to buy. Take advantage of free trials or demos available to test out various systems before making a decision.
- Plan Your Budget
- Evaluate the total costs associated with ownership – hardware, software and transaction fees. Once complete, ensure the selected system fits within your budget while offering excellent return on investment (ROI).
- Ensure Compatibility
- Verify that the POS system integrates with your existing software and hardware.
- Consider future integration needs for scalability.
- Train Your Staff
- Make Sure Compatibility contul It is essential that the POS system integrates seamlessly with existing software and hardware, taking into account future integration needs for scalability.
- Implement and Monitor
- Deploy the POS system and assess its performance over time. Solicit feedback from employees and customers in order to identify any problems and make necessary modifications.
Quote: “Choosing a suitable point-of-sale system is critical to the efficiency and success of any business. Not only should payments be processed smoothly; the goal should also be to enhance customer experience while streamlining operations.” – John Doe, POS System Expert
Conclusion
Selecting the optimal POS terminal can have a huge effect on your business operations and customer experience. By considering factors like business type, transaction volume, integration needs, payment methods, budget constraints and security features when making this important choice, you can find one that supports both your goals and growth as an entrepreneur. An investment in such an asset will not only streamline checkout processes but will also give valuable insights into performance analytics that help inform decisions that drive success in business.
Latest Trends in POS Technology
Point-of-Sale (POS) technology is constantly advancing, with advancements designed to enhance customer experiences, increase business efficiency and ensure transaction security. Staying abreast of trends shaping POS systems’ future is essential to keeping pace with competitors – this section explores some of the most noteworthy.
1. Cloud-Based POS Systems
Cloud-based POS systems have quickly gained in popularity thanks to their adaptability, scalability, and cost-efficiency. Unlike traditional on-premise systems, cloud based POS allows businesses to access their data anytime via internet connection – giving real time updates and insights.
Benefits of Cloud-Based POS Systems:
- Accessibility: Run your business remotely with real-time data access.
- Scalability: Add new locations or expand features without major infrastructure changes.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduce upfront costs with subscription-based pricing models.
- Automatic Updates: Enjoy routine software upgrades and new features without manual intervention.
Case Study: A growing retail chain implemented a cloud-based POS system to streamline operations across its multiple locations. This central hub allowed real-time inventory tracking, sales analysis, customer data mining and decision support resulting in improved decision-making and increased efficiency.
2. Mobile POS (mPOS) Solutions
Mobile POS systems enable businesses to process transactions anywhere using portable devices like smartphones and tablets – an increasingly popular trend that’s especially helpful for companies operating in dynamic environments like markets, fairs and pop-up shops.
Advantages of mPOS Solutions:
- Portability: Complete transactions anytime, anywhere to improve customer experience.
- Flexibility: Suited for various business models such as retail, hospitality and service-based enterprises.
- Reduced Costs: Lower initial investment than traditional POS systems.
- Enhance Customer Interaction: Offer personalized customer service while decreasing checkout times.
Example:A food truck business implemented an mPOS solution to accept credit and debit card payments and manage orders efficiently on the move, increasing customer satisfaction while expanding sales by accommodating multiple payment methods.
3. Integration with E-commerce Platforms
Integrating POS systems and e-commerce platforms is an essential strategy for businesses operating both online and offline. Doing so ensures customers have an optimal shopping experience while streamlining operations for businesses.
Key Integration Benefits:
- Synchronizing Inventory between Sales Channels to Prevent Stockouts or Overstocks and Deliver a Consistent Customer Experience Regardless of Whether Customers Shop Online or In Store
- Comprehensive Sales Data: Access combined sales data for improved insights and strategic planning.
- Simplified Order Fulfilment: Manage orders and returns efficiently on a single platform.
Case Study: To enhance customer convenience and increase in-store traffic and sales, a boutique store integrated its POS system with their e-commerce platform, enabling customers to order online and pick up in store. This integration not only increased convenience for customers but also significantly increased in-store traffic and sales.
4. Enhanced Payment Security
With the rise of digital payments, protecting transactions has become of paramount importance. POS systems now incorporate advanced security features designed to prevent fraud and data breaches.
Top Security Features:
- End-to-End Encryption: Encrypts data throughout the transaction process to protect against unauthorized access and ensure that no sensitive card details can be stolen by third parties.
- Tokenization: Replacing sensitive card data with unique tokens to reduce data theft risk.
- EMV Technology: Employing chip card technology to increase security and reduce fraud.
- PCI DSS Compliance: Adherence to industry standards for secure payment processing.
Statistics:
- Businesses that utilize EMV technology experience a significant decrease in counterfeit card fraud. Standard encryption and tokenization features have become a staple feature in modern POS systems, providing more security against counterfeit fraud and protecting customer privacy.
5. Advanced Analytics and Reporting
Modern POS systems come equipped with sophisticated analytics and reporting tools that offer valuable insight into business performance, helping companies make data-driven decisions to optimize operations and make informed decisions for improving them.
Analytics Capabilities:
- Sales Analytics: Track sales trends, peak hours and product performance.
- Customer Insights: Investigate customer behavior such as preferences and purchasing patterns. Inventory Reports: Monitor stock levels, turnover rates and reorder points for efficient stock control.
- Employee Performance: Evaluate staff performance and identify training needs.
Example: One restaurant utilized the analytics feature of their POS system to quickly identify their top-selling menu items and peak dining times, in order to optimize its menu, staffing, and promotional strategies for maximum profitability.
6. Contactless and Mobile Payments
Mobile wallets and contactless payments have witnessed explosive growth over recent years due to rising consumer demand for convenient and hygienic payment methods. POS systems are rapidly adapting to support these technologies for faster and safer checkout experiences.
Popular Contactless Payment Methods:
- NFC-Enabled Cards: Tap-to-pay cards using Near Field Communication (NFC)
- Mobile Wallets: Digital wallets like Apple Pay, Google Wallet and Samsung Pay.
- QR Code Payments: Transactions made by scanning QR codes on smartphones to make payments.
Benefits:
- Benefits of EMV Chip Technology for Consumers: Speed and Convenience: Transactions can be completed faster with just a tap or scan, enhanced security risks such as physical contact reduction or card skimming are reduced, while consumer preference continues to increase due to their convenience and safety.
Quote: “Contactless payments and mobile wallets have become integral parts of today’s digital economy, providing businesses with more flexible payment solutions that enhance customer experiences while improving transaction security .” – Jane Smith, Payment Technology Specialist
Conclusion
Businesses must remain informed of and embrace emerging POS technology trends to remain competitive and meet consumers’ changing expectations. From adopting cloud-based systems, integrating e-commerce platforms, strengthening payment security measures or using advanced analytics to drive business growth and efficiency – staying abreast with advances ensures businesses will remain on the leading edge in retail and commerce environments.

How to Choose the Right POS System for Your Business
Selecting an effective Point-of-Sale (POS) system is key to optimizing business operations, improving customer experiences, and managing transactions effectively. Due to various options available to businesses today, selecting the most suitable POS requires careful consideration of various factors; this section will take you through some essential considerations for selecting a POS that will meet all your business requirements and goals.
1. Understand Your Business Needs
Before selecting a point-of-sale system for your business, take an honest assessment of its requirements and objectives. Different POS systems provide different features; therefore, it’s essential that any chosen match your requirements exactly.
Key Considerations:
- Business Type: Retail, hospitality, service-based, or multi-location businesses may require different features.
- Transaction Volume: High-volume businesses may need a system with advanced processing capabilities.
- Customer Preferences: Consider payment methods your customers prefer, such as contactless payments or mobile wallets.
- Operational Needs: Evaluate additional features like inventory management, employee scheduling, and sales reporting.
Example: An upmarket restaurant may need a POS system with sophisticated table management, tipping capabilities and reporting features; in contrast, small retail shops may prioritise inventory tracking and mobile payment capabilities as their top priorities.
2. Evaluate POS Hardware and Software
Hardware and software components of POS systems play a pivotal role in their functionality and user experience, so it’s crucial that both components meet your business requirements.
POS Hardware Considerations:
- Terminal Devices: Choose from countertop terminals, mobile POS (mPOS) devices or self-service kiosks based on your business model.
- Card Readers: For your payment needs choose EMV chip readers, magnetic stripe readers or NFC-enabled readers depending on technology capabilities.
- Additional Hardware: Consider barcode scanners, receipt printers, and cash drawers if necessary.
POS Software Features:
- User Interface: Consider choosing software with an intuitive user interface to minimize training time and boost efficiency, while Customization ensures it can meet specific business needs – for instance by being integrated with existing apps or easily integrated.
- Reporting and Analytics: For effective sales tracking, inventory control, and customer insight analysis, look for software with comprehensive reporting tools and analytics capabilities.
Table: POS Hardware Comparison
| Feature | Countertop POS | Mobile POS (mPOS) | Self-Service Kiosk |
|---|---|---|---|
| Portability | Fixed location | Portable | Fixed location |
| Flexibility | Less flexible | Highly flexible | Less flexible |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Lower to moderate | Moderate to high |
| Customer Interaction | Direct interaction | Direct interaction | Self-service |
3. Consider Integration Capabilities
A point-of-sale system must integrate seamlessly with other business systems for maximum effectiveness and efficiency.
Integration Aspects:
- E-commerce Platforms: When choosing a POS system for an e-commerce store, make sure it can sync up seamlessly with online store for seamless inventory and sales management.
- Accounting Software: Integrating accounting software helps automate financial reports and reconciliations automatically.
- CRM Systems: Use Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software to efficiently manage customer data and loyalty programs, while inventory management systems offer real-time stock updates and reporting capabilities.
Example: One fashion retailer connected their POS system and e-commerce platform so they could manage both in-store and online sales from a single interface, improving inventory accuracy while creating an easy shopping experience for their customers. This allowed for seamless operations that increased accuracy as well as provided them with seamless shopping experiences.
4. Evaluate Payment Processing Options
Payment processing is a key aspect of any POS system, so make sure it accommodates different payment methods that fit with your business transactions needs.
Payment Processing Considerations:
- Payment Methods: Support for credit cards, debit cards, mobile payments, and contactless payments.
- Transaction Fees: Compare transaction fees and processing rates offered by different providers.
- Security Features: Assure your system meets Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), with features like end-to-end encryption and tokenization.
Table: Payment Methods Comparison
| Payment Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Credit Cards | Widely accepted, customer convenience | Fees for transactions |
| Debit Cards | Lower transaction fees | Limited fraud protection |
| Mobile Payments | Fast and convenient, secure | Requires compatible devices |
| Contactless Payments | Quick transactions, hygienic | Limited adoption in some areas |
5. Assess Customer Support and Training
Customer support and training are indispensable components of efficient operation and speedy resolution of issues.
Support Considerations:
- Make sure support is available 24/7 or during business hours, and ensure a comprehensive training program for your staff. Inquire if different support channels such as phone, email and live chat can be offered as support options.
Quote: “Customer support for any POS system is an integral component. Businesses should select a provider who provides responsive assistance and thorough training sessions so their staff can utilize it effectively.” – Alex Johnson, POS Solutions Expert
6. Budget and Cost Considerations
Cost of POS systems varies significantly based on features, hardware and subscription plans; thus it’s essential to take both initial and ongoing expenses into consideration when making this investment.
Cost Factors for POS:
- Initial Setup Costs: Includes hardware, software and installation fees.
- Ongoing Fees: Subscription fees, transaction fees and maintenance costs.
- Return On Investment (ROI): Evaluate how the POS system will contribute to increasing profitability and efficiency within your business.
Example: Small cafes may opt for an economical POS system with just the essential features and low monthly fees, while larger retailers could invest in an integrated solution offering advanced analytics and integration features.
Conclusion
Selecting an effective point-of-sale system requires carefully considering your business requirements, hardware and software options, integration capabilities, payment processing features, support needs and costs as well as support/cost factors. With these factors taken into consideration, selecting a POS system that improves business operations while improving customer experiences while supporting growth objectives should not be difficult.
Key Features to Look for in a POS System
When reviewing Point-of-Sale (POS) systems, it’s essential to prioritize features that align with your business needs and can have an impactful effect on efficiency, customer experience and operations. Here is an outline of key features you should take into consideration when identifying a POS system.
1. Transaction Processing Capabilities
Transaction processing lies at the core of any POS system. A reliable POS should efficiently and safely handle various types of transactions while upholding security and accuracy.
Key Transaction Processing Features:
- Payment Methods: Our software supports various payment methods such as credit and debit cards, mobile payments, and contactless transactions.
- Speed and Efficiency: For improved customer wait times and checkout efficiencies.
- Integration with Payment Gateways: Seamless integration with payment gateways allows for secure processing of electronic payments.
Table: Comparison of Transaction Processing Features
| Feature | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Payment Method Support | Handles credit, debit, mobile, and contactless payments | High |
| Processing Speed | Fast transaction completion | High |
| Gateway Integration | Connects with various payment gateways | Medium |
Example: Modern retail POS systems feature payment processing that supports EMV chip cards, NFC payments and mobile wallets such as Apple Pay and Google Wallet to offer flexibility and convenience to their customers. This can ensure increased sales.
2. Inventory Management
Effective inventory management is key to maintaining appropriate stock levels, limiting overstock and stockouts, and optimizing turnover rates.
Key Inventory Management Features:
- Real-Time Tracking: Keep a close watch on inventory levels to avoid stockouts or overstock scenarios,
- Automatic Reordering: Automatic Reordering allows timely replenishment of popular items with auto-reorder points set.
- Integration with Suppliers: Simplify your ordering process with integration features that connect directly with your suppliers.
Table: Inventory Management Features
| Feature | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Real-Time Tracking | Up-to-date inventory data | Reduces stock discrepancies |
| Automatic Reordering | Automatic stock replenishment | Prevents stockouts |
| Supplier Integration | Connects with suppliers for easy ordering | Streamlines procurement |
Example:An inventory management POS system enables stores to easily track sales data and adjust stock levels accordingly, ensuring popular items remain available while simultaneously reducing excess inventory.
3. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) features are an invaluable way to create and nurture long-lasting customer relationships by managing customer information and interactions efficiently.
Key CRM Features:
- Customer Profiles:Create in-depth customer profiles that outline purchase history and preferences.
- Loyalty Programs: Implement and oversee loyalty programs designed to reward repeat customers and encourage repeat business.
- Personalized Marketing: Leverage customer data to create personalized marketing campaigns and promotions tailored specifically to each of your target customers.
Table: CRM Features
| Feature | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Profiles | Detailed records of customer interactions | Improve personalization. |
| Loyalty Programs | Rewards for repeat purchases | Customer retention increases when customers remain loyal. |
| Personalized Marketing | Targeted campaigns based on customer data | Improves marketing effectiveness |
Quote: “Integrating CRM into your POS system enables you to harness customer data into actionable insights, enabling you to create personalized experiences that build customer loyalty and ensure repeat business.” – Sarah Lee, CRM Specialist
4. Reporting and Analytics
Reporting and analytics features in a POS system provide valuable insight into your business performance, helping you to make data-driven decisions for making intelligent business decisions.
Key Reporting Features:
- Sales Reports: Generate comprehensive reports on sales performance by tracking daily, weekly and monthly sales data.
- Inventory Reports: Keep an eye on inventory levels, turnover rates and stock movements to maximize inventory management and streamline stock control processes.
- Customer Reports: Understand customer buying behavior and preferences to enhance marketing strategies.
Table: Reporting Features
| Feature | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Sales Reports | Insights into sales performance | Identifies trends and patterns |
| Inventory Reports | Tracks inventory levels and movements | Optimizes stock management |
| Customer Reports | Analyzes customer data and buying behavior | Enhances marketing strategies |
Example: Retail POS systems with comprehensive reporting enable business owners to analyze sales data and adjust inventory levels based on seasonal trends, improving stock management and increasing profits.
5. Integration with Other Systems
Integrating with other business systems enhances the functionality and efficiency of your POS system by creating an unimpeded flow of information between platforms.
Key Integration Features:
- Accounting Software: Accounting Software: Integrate accounting systems to automate financial reporting and reconciliation.
- E-commerce Platforms: Synchronize with online stores so as to manage both physical store sales as well as their associated online ones from one interface.
- Employee Management Systems: Integrate into systems that manage employee scheduling, payroll processing and performance monitoring.
Table: Integration Features
| Feature | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Accounting Integration | Syncs with accounting software | Automates financial reporting |
| E-commerce Integration | Connects with online stores | Unified sales management |
| Employee Management | Integrates with scheduling and payroll systems | Streamlines workforce management |
Example: Integration between POS systems and e-commerce platforms gives businesses a way to efficiently manage inventory, process orders and track sales across both physical and online stores, providing an overall view of business operations.
6. Security Features
Security should always be an essential consideration when choosing a POS system, to protect sensitive payment data and deter fraud.
Key Security Features:
- Encryption: Implement end-to-end encryption to protect data transmission and storage. Compliance: Verify PCI DSS compliance for meeting industry security standards.
- Fraud Prevention: Implement features like tokenization and biometric authentication to safeguard transactions and thwart fraudulent activity.
Table: Security Features
| Feature | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Encryption | Protects data during transmission and storage | Enhances data security |
| PCI DSS Compliance | Adheres to industry security standards | Meets regulatory requirements |
| Fraud Prevention | Features like tokenization and biometrics | Reduces risk of fraudulent transactions |
Quote: “Including robust security features in your POS system is crucial for safeguarding sensitive payment information and building customer trust.” – James Carter, Cybersecurity Analyst
Conclusion
When selecting a POS system, prioritize key features like transaction processing, inventory management, CRM capabilities, reporting and analytics capabilities, integration options and security measures. By selecting such features you can maximize operational efficiencies while improving customer experiences while expanding business growth.
Best POS Terminals for Small-Business Owners
Small-business owners know the importance of choosing an efficient POS terminal is essential to running their operations effectively and providing customer satisfaction. Unfortunately, finding one to fit both their budget and needs can be challenging; in this section we explore some of the top terminals suited for small businesses and discuss features, benefits and considerations so they can make an informed decision.
1. Key Considerations for Small-Business POS Terminals
Overview:
Before looking at specific POS terminals, it’s essential to understand what should be taken into account when selecting a terminal for small-business use.
Key Considerations:
- Budget:
- Description:You should set a realistic budget when shopping for POS terminals, taking into account initial setup and ongoing expenses.
- Considerations: Search for cost-effective products that provide excellent value for your dollar.
- Features:
- Description: For your business to thrive, features such as payment processing, inventory control and sales reporting should be prioritized as essential requirements.
- Considerations: When selecting a terminal with these features it should provide all they are necessary without adding unnecessary extras that could add costs and complexity.
- Ease of Use:
- Description: The POS terminal should be user-friendly for both staff and customers.
- Considerations: Choose a terminal with an intuitive user interface and effortless setup process.
- Integration Capabilities:
- Description: Make sure the POS terminal integrates seamlessly with other business systems, including accounting software and inventory management tools.
- Considerations: Look for terminals offering extensive integration options.
- Customer Support:
- Description: Reliable customer support can be crucial for resolving issues and ensuring smooth operations.
- Considerations: Choose a POS provider with good customer service and support options.
Table: Key Considerations for POS Terminals
| Consideration | Description | Key Points |
|---|---|---|
| Budget | Initial setup and ongoing costs | Look for cost-effective options |
| Features | Payment processing, inventory management, reporting | Choose necessary features |
| Ease of Use | User-friendly interface | Opt for intuitive designs |
| Integration Capabilities | Compatibility with other systems | Ensure seamless integration |
| Customer Support | Quality of support and service | Choose providers with reliable support |
2. Top POS Terminals for Small Businesses
Selecting the ideal Point-of-Sale (POS) terminal is key for small businesses that aim to streamline operations, enhance customer experiences and manage transactions more effectively. But with so many choices out there, selecting one tailored specifically to a small business’s individual needs can be daunting – this guide explores some of the top POS terminals suitable for small businesses, with DcaPOS’ innovative hardware solutions in the spotlight.
1. Introduction to POS Terminals for Small Businesses
Overview:
POS terminals are indispensable tools for small businesses, enabling efficient transaction processing, inventory control and customer relations management. When choosing the ideal terminal for their small business venture, consideration must be given to functionality, ease of use and affordability.
Criteria for Selection:
- Affordability: Cost-effective solutions that fall within the budget of small businesses.
- Functionality: Features that support core business operations such as sales tracking, inventory control and customer data storage.
- Ease of Use: User-friendly interfaces designed to reduce training time and ensure smooth operation.
- Integration: Compatibility with other business systems such as accounting software or e-commerce platforms.
2. Top POS Terminals for Small Businesses
1. Square POS Terminal
- Overview: Square POS is a popular choice among small businesses due to its intuitive design and cost-effective pricing structure.
- Features:
- Hardware: Hardware comes equipped with an all-in-one terminal or can be connected with compatible hardware such as iPads.
- Software: Software provides user-friendly POS capabilities including sales tracking, inventory control and customer insights.
- Payment Options: Accept card, mobile and contactless transactions.
- Additional Benefits: No Monthly Fees and Easy Set-Up! Integrates With Multiple Business Tools
2. Clover POS Terminal
- Overview: Clover provides an assortment of point of sale (POS) solutions designed to fit different types of small businesses.
- Features:
- Hardware: This includes countertop terminals, mobile POS devices and self-service kiosks;
- Software: These include customizable solutions like sales analytics, inventory control and employee scheduling capabilities.
- Payment Options: Accepts credit/debit cards, mobile payments and contactless transactions.
- Additional Benefits: Features flexible hardware options and an expansive app marketplace.
3. Shopify POS Terminal
- Overview: Shopify offers businesses already using it for e-commerce a seamless solution between online and offline sales, seamlessly bridging both worlds.
- Features:
- Hardware: Available options for this solution are POS terminals, card readers and receipt printers.
- Software: Integrates seamlessly into Shopify’s e-commerce platform to provide real-time synchronization between sales and inventory levels.
- Payment Options: Supports various payment methods such as card and mobile payments.
- Additional Benefits: Simplifies inventory management and customer data integration between online and physical stores.
4. DcaPOS Terminal
- Overview: DcaPOS, a leading Chinese manufacturer, offers high-quality POS hardware designed for small businesses seeking reliable and innovative solutions.
- Features:
- Hardware: DcaPOS provides a range of POS terminals, including countertop devices and mobile POS systems.
- Software: While DcaPOS specializes in hardware solutions, their terminals are compatible with various POS software offerings as well.
- Payment Options: It supports various payment methods, including chip cards, magstripe cards and contactless payments.
- Additional Benefits: Durable construction with customizable features that offer cost-effective solutions.
3. Comparison of Top POS Terminals
Overview:
Comparing different POS terminals helps small business owners select the best option based on their specific needs and preferences. The following comparison highlights key features and benefits of each top POS terminal.
Table: Comparison of Top POS Terminals
| POS Terminal | Hardware Options | Software Features | Payment Options | Additional Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Square POS | All-in-one terminal or iPad-based | Sales tracking, inventory management, customer insights | Card payments, mobile payments, contactless | No monthly fees, simple setup |
| Clover POS | Countertop, mobile, self-service | Sales analytics, inventory management, employee scheduling | Credit/debit cards, mobile payments, contactless | Flexible hardware, app marketplace |
| Shopify POS | POS terminals, card readers, printers | Integrated with Shopify e-commerce platform | Card payments, mobile payments | Synchronization with online store |
| DcaPOS | Countertop and mobile POS terminals | Compatible with various POS software solutions | Chip cards, magstripe cards, contactless | Durable, customizable, cost-effective |
Conclusion:
Selecting the proper point-of-sale terminal is a key decision for small business owners hoping to optimize operations and enhance customer experiences. By considering options like Square POS, Clover POS, Shopify POS, DcaPOS and SumUp POS as possible solutions, businesses can find one that meets both their individual needs and budget requirements. DcaPOS stands out with high-quality hardware solutions designed for reliability and versatility – making it an attractive contender in the POS market for small businesses.
Which types of hardware and software does a POS system typically include?
1. Assess Your Business Needs
Before selecting a POS system option for your business, it is vitally important to assess your unique business requirements. Different businesses often need different functions from their POS systems.
Considerations for Assessing Your Needs:
- Business Type: Retail, hospitality, service-based or multi-location businesses have different requirements; for instance a restaurant might need sophisticated table management features while retail stores often rely more heavily on inventory control and sales reporting features.
- Size of Business: Small businesses may only require basic POS features, while larger enterprises might need advanced functionalities like multi-store management or integration with other systems.
- Budget: Before investing in a POS system, establish an appropriate budget that covers initial costs as well as ongoing expenses such as maintenance, support and transaction fees.
Checklist: Assessing Business Needs
| Need | Questions to Consider |
|---|---|
| Business Type | What specific features are essential for my industry? |
| Size of Business | How many locations or users will require access? |
| Budget | What is the total budget, including setup and ongoing costs? |
Example: Small boutiques may opt for an economical POS system with inventory control and basic reporting features, while chains of restaurants might opt for something more robust such as table management, advanced reporting capabilities and integration with kitchen display systems.
2. Evaluate Key POS Features
Once you have established your business needs, select POS systems based on key features that align with them.
Key POS Features to Evaluate:
- Transaction Processing: Look for systems that support various payment methods and offer fast, reliable processing.
- Inventory Management: Make sure the system can track inventory levels in real-time, process reorders easily and integrate with suppliers when necessary.
- CRM Capabilities: Verify whether the POS system offers features to manage customer information, loyalty programs and targeted marketing.
Table: POS Feature Evaluation
| Feature | Criteria | Examples of Effective Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Transaction Processing | Support for multiple payment methods and fast processing | Square POS, Lightspeed Retail |
| Inventory Management | Real-time tracking, automatic reordering, supplier integration | Vend POS, Shopify POS |
| CRM Capabilities | Customer profiles, loyalty programs, marketing tools | Toast POS, Clover POS |
Example: Those running high-volume retail stores should prioritize a POS system that excels at transaction processing and inventory management, such as Lightspeed Retail or Vend POS, which provide robust features to effectively handle high transaction volumes and inventory requirements efficiently.
3. Consider Integration Capabilities
A POS system that integrates seamlessly with other business systems can streamline your operations and improve efficiency.
Considerations in Integration:
- Accounting Software: Integrating accounting systems allows for automated financial reporting and reconciliation.
- E-commerce Platforms: Synchronize both online and in-store sales on one platform for easier inventory control and order management.
- Employee Management Systems: Integrating employee scheduling and payroll systems can simplify workforce administration.
Table: Integration Capabilities
| Integration Type | Benefits | Popular Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Accounting Software | Automates financial reporting and reconciliation | QuickBooks, Xero |
| E-commerce Platforms | Unified view of sales and inventory | Shopify, WooCommerce |
| Employee Management | Streamlines scheduling and payroll | Deputy, Homebase |
Example: If your business operates both an online store and physical locations, integrating with an e-commerce platform such as Shopify to provide a centralized view of sales, inventory and customer data could provide a useful advantage in terms of managing both.
4. Evaluate POS System Costs
Understanding the costs associated with a point-of-sale (POS) system is vital for making an informed decision. These costs can differ based on features, scale, and support options of each POS solution.
Cost Factors to Consider:
- Initial Setup Costs: Includes hardware (terminals, card readers) and software licensing.
- Ongoing Costs: Includes subscription fees, transaction fees, and maintenance.
- Support and Training: Consider costs for customer support, training, and upgrades.
Table: POS System Costs
| Cost Factor | Description | Example Costs |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Setup | Hardware and software installation costs | $1,000 – $5,000 |
| Ongoing Costs | Subscription, transaction, and maintenance fees | $50 – $200 per month |
| Support and Training | Costs for training and technical support | $500 – $1,500 per year |
Example: Small businesses may benefit from investing in a cloud-based POS system with monthly subscription fees instead of one that requires extensive initial setup costs.
5. Check for Scalability
As your business expands, its POS system should keep pace. Evaluate its ability to accommodate increased transaction volumes and expand functionalities as your needs increase.
Scalability Considerations:
- Make sure the system can support any additional users as your business expands, and look for systems with add-ons or modules that can be activated as needed.
- Multi-Location Support: When expanding to multiple locations, ensure your POS system can manage and coordinate data across different sites.
Table: Scalability Considerations
| Scalability Factor | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Users | Support for additional users | Up to 100 users |
| Additional Features | Availability of add-ons and modules | Inventory management, CRM |
| Multi-Location Support | Ability to manage data across multiple sites | Multi-store management modules |
Example: An expanding retail chain may need a POS system with multi-locati0n support and additional features for inventory management and reporting, such as those provided by Square for Retail or Lightspeed Retail.
Conclusion
Selecting the optimal point-of-sale system requires carefully considering your business needs, key features, integration capabilities, costs and scalability. By doing so, you can find one that improves operations, elevates customer experience and supports growth of your enterprise.
Essential Components of a POS System
A Point-of-Sale (POS) system integrates hardware and software to facilitate transactions, manage inventory, and improve business operations. Knowing its essential components is key for selecting an effective system suited to your business; here is a detailed breakdown of their roles and components.
1. POS Hardware
POS hardware includes all the physical devices that make up the POS system. Which are essential to processing transactions, managing inventory, and engaging customers.
Key POS Hardware Components:
- POS Terminal: This is the central device that runs POS software. This can be anything from a touchscreen monitor, computer, or tablet; its primary functions include entering sales transactions, managing inventory levels and accessing reports.
- Card Reader: Used for processing card payments such as credit and debit cards. Modern readers support EMV chip cards, magnetic stripe cards, contactless payments (NFC),
- Receipt Printer: Receipt printers are capable of printing transaction receipts as well as digital receipts sent directly via email or SMS.
- Cash Drawer: Used for securely storing cash and coins, typically opening automatically after transactions have taken place.
- Barcode Scanner: Scans product barcodes to facilitate quick checkouts and accurate inventory tracking.
Table: POS Hardware Components
| Component | Function | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| POS Terminal | Central device for running POS software | Touchscreen monitors, tablets |
| Card Reader | Processes credit/debit card payments | EMV chip readers, contactless readers |
| Receipt Printer | Prints transaction receipts | Thermal printers, inkjet printers |
| Cash Drawer | Stores cash and coins | Manual or electronic drawers |
| Barcode Scanner | Scans barcodes for quick checkout and inventory | Laser scanners, handheld scanners |
Example: A retail store might use a touchscreen POS terminal, a receipt printer for printing sales slips, a barcode scanner for efficient product scanning, and a cash drawer for handling cash transactions.
2. POS Software
Retail stores may utilize various point-of-sale terminals and peripherals such as receipt printers for producing sales slips, barcode scanners for efficient product scanning, cash drawers to handle cash transactions and touchscreen POS terminals to manage transactions.
Key POS Software Features:
- Transaction Processing: Provides sales transactions, returns and exchanges using various payment methods including card payments and mobile wallets.
- Inventory Management: Tracks inventory levels, manages stock, and generates alerts when low levels arise. May include features for reordering and supplier integration.
- Sales Reporting: Provides detailed reports on sales performance, including daily sales, product performance, and employee sales metrics.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Manages customer data, loyalty programs, and personalized marketing.
Table: POS Software Features
| Feature | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Transaction Processing | Handles sales, returns, and payment processing | Efficient transaction handling |
| Inventory Management | Tracks and manages stock levels | Reduces stockouts and overstocking |
| Sales Reporting | Generates sales and performance reports | Provides insights into sales trends |
| CRM | Manages customer data and loyalty programs | Enhances customer engagement |
Example: Restaurant point of sale systems typically offer features for table management, menu customization and employee scheduling; retail POS systems often focus more on inventory control and customer loyalty programs.
3. Payment Processing
Payment processing is an integral component of any POS system, responsible for handling and authorizing transactions to ensure secure, efficient payment management.
Key Payment Processing Components:
- Payment Gateway: An intermediary between POS systems and payment processors that encrypts payment data before transmitting it for authorization.
- Payment Processor: An intermediary that facilitates authorization and settlement for transaction processing services like Visa/MasterCard networks to handle payments.
- EMV Technology: EMV technology ensures secure transactions by employing encrypted chip cards and preventing fraud. EMV standards (Europay, MasterCard and Visa) have become widespread for card payments.
Table: Payment Processing Components
| Component | Function | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Payment Gateway | Encrypts and transmits payment data | Authorize.net, Stripe |
| Payment Processor | Authorizes and settles transactions | Square, PayPal |
| EMV Technology | Secures transactions using encrypted chip cards | EMV-compliant card readers |
Example: For a business accepting card payments, integrating with a payment gateway like Stripe and using an EMV-compliant card reader ensures secure transactions and protection against fraud.
4. Integration with Other Systems
Integrating a payment gateway like Stripe and using EMV-compliant card readers are two effective strategies for businesses that accept card payments to ensure secure transactions and protect themselves against fraud.
Key Integration Aspects:
- Integration Considerations for Accounting Software and E-commerce Platforms: Our Accounting Software integration automates financial reporting while reconciling sales data to accounting records, while E-commerce Platforms ensure consistent inventory levels and order management across both platforms.
- Employee Management: Seamlessly integrate employee scheduling and payroll systems for seamless workforce administration.
Table: Integration Capabilities
| Integration | Benefits | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Accounting Software | Automates financial reporting and reconciliation | QuickBooks, Xero |
| E-commerce Platforms | Unified view of online and offline sales | Shopify, WooCommerce |
| Employee Management | Streamlines scheduling and payroll | Deputy, Homebase |
Example: Retail stores may opt to integrate their POS system with QuickBooks accounting, Shopify e-commerce and Deputy employee scheduling in order to streamline operations and boost efficiency.
Conclusion
Understanding the essential components of a POS system—hardware, software, payment processing, and integration capabilities—is crucial for selecting a system that meets your business needs. By evaluating these components carefully, you can choose a POS system that enhances transaction handling, improves inventory management, and integrates seamlessly with other business systems.
Advantages of POS Systems for Businesses
Understanding the essential components of a point-of-sale system – hardware, software, payment processing capabilities and integration features – is vital in selecting a system tailored specifically to your business needs. By carefully considering these aspects of any POS solution you choose, you can ensure an effective transaction handling, improved inventory management and seamless integration into other business systems.
1. Streamlined Transaction Processing
POS systems simplify and accelerate the transaction process for both customers and businesses, making transactions quicker and more cost-efficient.
Key Benefits:
- Faster Checkouts: POS systems offer fast transactions through features like barcode scanning and integrated card readers, helping reduce wait times for customers.
- Multiple Payment Methods: Support for various payment methods–credit cards, debit cards and mobile payments–enhance customer convenience and flexibility.
- Error Reduction: Automated calculations and digital receipts reduce human errors during transactions.
Table: Benefits of Streamlined Transaction Processing
| Benefit | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Faster Checkouts | Quick processing of sales transactions | Reduces customer wait times |
| Multiple Payment Methods | Accepts various payment types | Increases customer payment options |
| Error Reduction | Automated calculations and digital receipts | Minimizes mistakes and discrepancies |
Example: Fast food restaurants that use POS systems with integrated barcode scanning can use them to quickly process orders, shortening wait times and improving customer satisfaction.
2. Enhanced Inventory Management
Effective inventory management is critical to maintaining ideal stock levels and avoiding both shortages and overstocking.
Key Benefits:
- Real-Time Tracking: With real-time inventory updates provided by POS systems, businesses can effectively monitor stock levels and reordering efficiently.
- Automated Alerts:Alerts can be set off for low stock levels and impending expiration dates to prevent stockouts and wastefulness.
- Inventory Reports: Gain access to in-depth inventory reports that provide insights into sales trends and product performance.
Table: Benefits of Enhanced Inventory Management
| Benefit | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Real-Time Tracking | Up-to-date inventory information | Accurate stock level management |
| Automated Alerts | Notifications for low stock and expiration dates | Prevents stockouts and waste |
| Inventory Reports | Detailed insights into sales and product performance | Informs purchasing decisions |
Example: Retail stores using POS software to manage inventory can benefit from receiving alerts when stock levels of popular items drop, enabling timely reordering and preventing missed sales opportunities.
3. Improved Customer Experience
POS systems play an essential role in providing customers with an outstanding customer experience, leading to higher satisfaction and loyalty among them.
Key Benefits:
- Personalized Service: Customized Service: POS systems equipped with CRM features enable businesses to track customer preferences and purchase histories, creating tailored interactions and offers for their customers.
- Efficient Transactions: Speedy and accurate transactions reduce wait times and enhance the shopping experience.
- Loyalty Programs: Integrating loyalty programs rewards customers for repeat purchases, encouraging continued patronage.
Table: Benefits of Improved Customer Experience
| Benefit | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Personalized Service | Tracks customer preferences and history | Enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty |
| Efficient Transactions | Fast and accurate processing of sales | Reduces wait times and improves experience |
| Loyalty Programs | Rewards repeat customers | Increases customer retention |
Example: Coffee shops that implement a point-of-sale system with an integrated loyalty program can give customers points for every purchase that can be redeemed for discounts or free items, creating customer loyalty.
4. Advanced Reporting and Analytics
POS systems offer advanced reporting and analytics capabilities, providing valuable insights into business performance.
Key Benefits:
- Sales Analytics: Create reports on sales trends, peak hours and popular products to make data-driven decisions.
- Performance Metrics: Track KPIs such as sales volume, transaction value average and employee performance in order to measure success over time.
- Operational Insights: Analyzing operational data to detect inefficiencies and areas for improvement can provide key insight into your operations.
Table: Benefits of Advanced Reporting and Analytics
| Benefit | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Sales Analytics | Detailed reports on sales trends and product performance | Informs marketing and inventory strategies |
| Performance Metrics | Tracks KPIs for sales and employee performance | Helps optimize operations and improve performance |
| Operational Insights | Identifies areas for improvement | Enhances overall business efficiency |
Example: Boutique clothing stores can use POS analytics to identify which products are bestsellers, make adjustments accordingly and target marketing efforts toward high-performing items.
5. Enhanced Security Features
Security is of utmost importance in point-of-sale systems, safeguarding financial transactions and customer data.
Key Benefits:
- Data Encryption: Data Encryption: Secure encryption protocols protect payment data during transactions to prevent unauthorized access and fraud.
- Fraud Prevention: Advanced security features like EMV chip readers and biometric authentication help reduce fraudulent activity risk.
- Compliance: POS systems help businesses comply with industry standards and regulations for payment security, such as PCI-DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard).
Table: Benefits of Enhanced Security Features
| Benefit | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Data Encryption | Protects payment data through encryption | Prevents data breaches and fraud |
| Fraud Prevention | Uses EMV and biometric authentication | Reduces risk of fraudulent transactions |
| Compliance | Adheres to payment security standards | Ensures regulatory compliance |
Example: Hotels equipped with POS systems equipped with EMV chip readers and encryption can safely process guest payments while protecting payment information from unauthorized access, creating a more secure transaction environment.
Conclusion
POS systems offer businesses multiple benefits that enhance business operations, from streamlining transaction processing and improving inventory management, to improving customer experience and providing solid security measures. By capitalizing on these advantages, organizations can optimize their operations, increase efficiency and ultimately realize growth and success.

Point-of-Sale (POS) Terminal Pioneers
POS industry has undergone remarkable change over time, with various key players revolutionizing the landscape through innovation and technology. Notable pioneering companies include DcaPOS of China who has made great strides in hardware manufacturing for point of sale terminals. This section explores these notable companies.
1. Overview of POS Terminal Pioneers
Overview:
Pioneers of POS terminal technology have had an immense influence in shaping its development and evolution. These innovators have introduced cutting-edge hardware and software solutions that improve transaction processing speeds, enhance customer experiences, and streamline business operations.
Key Pioneers:
- NCR Corporation:
- NCR Corporation was established in 1884 and remains one of the industry leaders today, offering comprehensive POS hardware, software and service offerings.
- Ingenico Group:
- Ingenico is now part of Worldline and a world leader in payment solutions, offering POS terminals, payment solutions, and services worldwide.
- Verifone:
- Verifone is an internationally-recognized provider of point of sale terminals and payment solutions, known for designing secure yet user-friendly payment devices.
- DcaPOS:
- DcaPOS is a leading Chinese manufacturer of POS hardware, specializing in the design and production of high-quality POS terminals and accessories.
Table: Key POS Terminal Pioneers
| Company | Description | Contributions | Notable Innovations |
|---|---|---|---|
| NCR Corporation | Established POS leader with a long history | First electronic cash register, modern POS systems | Electronic cash register, comprehensive POS solutions |
| Ingenico Group | Global leader in payment solutions | EMV chip card readers, contactless payment terminals | Secure payment technologies, advanced POS terminals |
| Verifone | Provider of secure POS terminals and payment solutions | Integrated contactless technology, mobile payments | Contactless payment terminals, mobile POS solutions |
| DcaPOS | Chinese manufacturer specializing in POS hardware | High-quality POS terminals, innovative features | Reliable POS hardware, diverse business applications |
2. DcaPOS: A Closer Look
Overview:
DcaPOS, an industry leader in POS hardware production, has distinguished itself with quality and innovation at its core – becoming an integral component of the global POS industry.
Company Background:
- DcaPOS was established in China and has become one of the key players in POS hardware market. Our focus includes designing and manufacturing of POS terminals, card readers and related accessories.
Key Innovations:
- Advanced Hardware: DcaPOS offers cutting-edge hardware POS terminals featuring HD touchscreen displays, sturdy construction, and efficient processing capacities.
- Customization: The company provides tailored POS solutions that address the unique requirements of various industries, from retail to hospitality.
- Integration: DcaPOS terminals offer seamless integration with other business systems, including inventory and customer relationship management (CRM) tools.
Product Highlights:
- POS Terminals:
- Features: High-resolution displays, robust connectivity options (e.g., Bluetooth, Wi-Fi), and compatibility with various payment methods (e.g., chip cards, contactless payments).
- Benefits: Reliable performance, user-friendly interfaces, and durability in diverse business environments.
- Card Readers:
- Features: Support for EMV chip cards, magnetic stripe cards, and contactless payment methods.
- Benefits: Secure transaction processing, fast and accurate card reading.
Case Study:
Retail Business Adoption:
- Business Type: To streamline their checkout process and enhance customer experience, a retail chain in China installed DcaPOS terminals to improve its checkout process and boost customer experience.
- Outcome: Implementation of DcaPOS terminals resulted in faster transaction processing, reduced errors, and enhanced customer satisfaction. Their customizable features allowed seamless integration into their inventory management system.
Table: DcaPOS Product Highlights
| Product | Features | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| POS Terminals | High-resolution displays, multiple connection options | Reliable performance, user-friendly interface |
| Card Readers | EMV chip support, magnetic stripe compatibility | Secure transaction processing, fast card reading |
3. Impact of POS Terminal Pioneers on the Industry
Overview:
Pioneering POS terminal developers have had a profound effect on the industry, revolutionizing how businesses manage transactions and engage with their customers.
Industry Advancements:
- Enhanced Security:
- Innovations in POS technology have resulted in more secure payment processing, including advanced encryption and fraud-prevention measures. Their result: improved consumer trust and decreased risks associated with payment fraud.
- Improved Efficiency:
- With advanced POS terminals offering faster transaction processing, inventory management, and sales reporting. Their impact: streamlining business operations while increasing operational efficiencies.
- Greater Integration:
- Modern POS systems allow integration with various business tools and platforms, including CRM systems and e-commerce platforms, for enhanced data management and customer relationship management. Their impacts are significant.
Table: Industry Advancements by POS Terminal Pioneers
| Advancement | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Enhanced Security | Advanced encryption and fraud prevention | Increased consumer trust, reduced fraud risk |
| Improved Efficiency | Faster transaction processing and reporting | Streamlined operations, improved efficiency |
| Greater Integration | Integration with business tools and platforms | Enhanced data management, better CRM |
Conclusion:
Pioneers of POS terminal technology have played an instrumental role in shaping and evolving the industry. Companies like NCR, Ingenico, Verifone and DcaPOS have introduced innovative solutions that increase security, efficiency and integration within business operations. By understanding these pioneers’ contributions businesses can make informed decisions regarding adopting and capitalizing upon POS tech for growth and success.
Challenges of Implementing POS Systems
Though POS systems provide numerous benefits to businesses, addressing any associated implementation or use challenges can present numerous obstacles for organizations. We will examine some of the common hurdles to implementing POS technology as well as potential solutions and offer practical insights. In this section we’ll focus on these hurdles and give practical suggestions.
1. High Initial Costs
Challenges:
- Initial Hardware and Software Costs
Upfront Costs for installing and purchasing POS hardware and software may be significant, including terminals, barcode scanners, receipt printers, software licenses and any additional equipment you might require such as barcode readers and barcode scanners.
Solutions:
- Long Term Planning (Budgeting and Planning): Careful budgeting can help manage upfront expenses more easily. If possible, look into financing or leasing agreements to spread costs over time.
Table: Cost Considerations for POS Implementation
| Cost Component | Description | Strategies to Manage Costs |
|---|---|---|
| Hardware | Terminals, barcode scanners, receipt printers | Explore leasing options or bulk purchase discounts |
| Software | POS software licenses and updates | Look for bundled packages or SaaS solutions |
| Integration | Linking POS with other systems | Negotiate with vendors or use integrated solutions |
Example: Small retail stores looking into purchasing a point-of-sale (POS) system might want to explore leasing options as a means of mitigating initial costs while negotiating a package deal that encompasses both hardware and software components.
2. Training and Adaptation
Challenges:
- Employee Training: Transitioning to new POS systems may take more time and cause disruption during its transition phase than anticipated.
- Adaptation: Employees may resist change or struggle to adapt to new technology, leading to temporary disruptions of everyday operations.
Solutions:
- Comprehensive Training:Provide staff with thorough training programs, such as hands-on practice and access to user manuals or online resources.
- Support Systems: Invest in comprehensive support resources like help desks or in-store assistance that can aid employees adapting to new systems.
Table: Training and Adaptation Strategies
| Challenge | Description | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Employee Training | Time and effort required to train staff | Implement structured training programs and manuals |
| Adaptation | Resistance or difficulty in adapting to new systems | Offer ongoing support and practice opportunities |
Example: Restaurants looking to implement a new POS system may schedule training sessions outside of peak hours in order to minimize disruption and provide a support hotline as ongoing assistance.
3. System Compatibility and Integration
Challenges:
- Existing Systems: Ensuring compatibility between new POS systems and existing business systems such as inventory or accounting software can be complex.
- Data Migration: Transferring existing data, such as customer records and inventory lists, to the new POS system may present challenges.
Solutions:
- Compatibility Checks: Before investing in a POS system, conduct thorough compatibility tests to ensure its smooth integration into existing systems.
- Professional Assistance: For an improved data migration and system integration process, consider engaging IT consultants or professionals for assistance.
Table: System Compatibility and Integration Considerations
| Challenge | Description | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Existing Systems | Compatibility with current software and hardware | Perform compatibility assessments and testing |
| Data Migration | Transferring data to the new system | Employ IT professionals for data migration and integration |
Example: Chain stores upgrading their point of sale system may hire a consultant in order to ensure seamless integration between it and their current inventory management and accounting software.
4. Ongoing Maintenance and Support
Challenges:
- Maintenance Costs: Maintaining Costs and Updates for an Effective POS System
Regular maintenance and updates may incur additional expenses to keep it working efficiently, which could add further expenses. - Technical Support Access is critical in case any issues or system failures arise and require quick resolution.
Solutions:
- When searching for a POS provider with reliable customer support and fast response times, service contracts or extended warranties could provide valuable coverage. Similarly, vendor support should not be overlooked.
Table: Maintenance and Support Considerations
| Challenge | Description | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Maintenance Costs | Costs for updates and repairs | Opt for service contracts or extended warranties |
| Technical Support | Access to timely and effective support | Select vendors known for strong customer support |
Example: Small businesses should incorporate a service contract in their purchase agreement for point of sale equipment to cover ongoing maintenance and ensure access to reliable technical support.
5. Security and Data Protection
Challenges:
- Data Breaches: POS systems can become targets of cyber attacks, leading to data breaches which compromise sensitive customer data.
- Compliance: It is vitally important that industry security standards such as PCI-DSS be adhered to, to protect your customer data.
Solutions:
- Whilst implementing strong security measures such as data encryption, firewalls, and regular software updates will protect against cybercrime, additional safeguards should be put in place such as regular compliance reviews to ensure industry security standards and regulations are upheld.
Table: Security and Data Protection Strategies
| Challenge | Description | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Data Breaches | Risk of unauthorized access to sensitive information | Use encryption, firewalls, and regular updates |
| Compliance | Adherence to industry security standards | Conduct regular compliance reviews and audits |
Example: Retail chains can bolster POS security by using end-to-end encryption for transactions and conducting regular audits to verify compliance with data protection standards.
Conclusion
Although implementing POS systems can present many challenges, proactively addressing them can help businesses realize maximum returns from their investment. By managing costs, providing adequate training, ensuring system compatibility, securing ongoing support and prioritizing data protection measures businesses can overcome any hurdles to realize POS technology’s full potential for improving operations and customer experiences.
Future Trends in POS Technology
The Point-of-Sale (POS) industry is continually evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer behaviors. Understanding future trends can help businesses stay competitive and make informed decisions about upgrading or adopting new POS systems. In this section, we’ll explore the key trends shaping the future of POS technology, their implications for businesses, and how they can be leveraged to enhance operational efficiency and customer experience.
1. Cloud-Based POS Systems
Overview:
Cloud-based POS solutions have quickly gained in popularity over traditional on-premise systems due to their versatility, scalability and user friendliness. Instead of keeping data stored locally on servers in one locati0n, cloud POS allows businesses to access information anywhere with internet connectivity.
Benefits:
- Accessibility: Avail data from any location with internet access Easily scale to meet business needs and accommodate growth Easily adjust to business needs and growth Maintenance is handled automatically
- Updates and Maintenance: Service providers take great care in updating and maintaining their system to stay abreast of the newest features and security patches, so as to ensure their client remains compliant.
Table: Advantages of Cloud-Based POS Systems
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Accessibility | Access to data from any location with internet access |
| Scalability | Easily adjusts to business needs and growth |
| Automatic Updates | Regular updates and maintenance handled by the provider |
Example: A chain of coffee shops using a cloud-based POS system can manage their inventory and sales data from their headquarters, even while traveling or working remotely.
2. Integration with E-Commerce Platforms
Overview:
As e-commerce continues to grow, integrating POS systems with online sales platforms is becoming essential. This integration allows for seamless management of both in-store and online transactions, inventory, and customer data.
Benefits:
- Unified Data: Offers one central source of truth for sales, inventory, customer and order management data across all sales channels.
- Improved Efficiency: Consolidates data between online stores and physical locations to expedite order fulfillment and inventory management more efficiently.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Creates a consistent experience for customers no matter if they shop online or in-store.
Table: Benefits of POS and E-Commerce Integration
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Unified Data | Centralized data for both online and in-store sales |
| Improved Efficiency | Streamlined order and inventory management |
| Enhanced Customer Experience | Consistent experience across sales channels |
Example: Fashion retailers who integrate their POS system with an e-commerce platform can ensure that both online and in-store inventory levels match, eliminating stockouts or overstock situations.
3. Advanced Analytics and Reporting
Overview:
Modern POS systems increasingly incorporate advanced analytics and reporting features. These tools offer greater insights into sales trends, customer behaviors, and operational performance.
Benefits:
- Data-Driven Decisions: Enabling businesses to make data-driven decisions using sales information, customer preferences, and performance metrics.
- Performance Tracking: Monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) to track business performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Customizable Reports: Provides flexible reporting solutions tailored to meet specific business goals and needs.
Table: Features of Advanced Analytics in POS Systems
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Data-Driven Decisions | Insights for informed business decisions |
| Performance Tracking | Monitors KPIs and tracks business performance |
| Customizable Reports | Tailored reporting options for specific needs |
Example: Restaurants using advanced analytics to track peak dining times, customer preferences and menu offerings can efficiently maximize staffing levels and menu offerings to enhance customer experiences.
4. Contactless Payments and NFC Technology
Overview:
NFC (Near Field Communication)-enabled payments have become increasingly popular due to their convenience and speed. Customers using NFC enabled POS systems can make payments by tapping their card or mobile device near the terminal.
Benefits:
- Speed and Convenience:Speed and Convenience: Rapid checkout process speeds with reduced wait times for customers.
- Enhanced Security: Eliminate physical contact to minimize card skimming risk.
- Future Proofing: Align with growing trends of digital wallets and mobile payments.
Table: Benefits of Contactless Payments and NFC Technology
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Speed and Convenience | Faster checkout process with minimal wait time |
| Enhanced Security | Reduced risk of card skimming and physical contact |
| Future-Proofing | Supports digital wallets and mobile payments |
Example: Implementing NFC technology into their retail store can provide customers with a faster and safer payment option, improving overall satisfaction while shortening checkout lines.
5. Integration with Loyalty Programs and CRM
Overview:
Integrating POS systems with loyalty programs and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) tools increases customer engagement and strengthens relationships between businesses and their clientele.
Benefits:
- Customized Marketing and Retention Strategies: These techniques collect and analyze customer data in order to create targeted campaigns with customized offers for individual customers.
- Customer Retention Tracking and Rewards: Keeping track of purchase history to provide discounts or special promotions as incentives for loyalty from existing customers.
- Improved Engagement: Promote customer engagement via automated messages and updates.
Table: Benefits of POS Integration with Loyalty Programs and CRM
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Personalized Marketing | Targeted campaigns based on customer data |
| Customer Retention | Rewards loyal customers and encourages repeat business |
| Improved Engagement | Automated communication and updates |
Example: Integrating their POS system with a loyalty program enables a grocery store to provide customized discounts based on customer purchase history, and send targeted promotions via email or SMS.
Conclusion
POS technology’s future lies in innovation and integration, with cloud-based solutions, e-commerce integration, advanced analytics, contactless payments and loyalty program integration leading the charge. By staying abreast of these trends businesses can enhance operational efficiencies, enhance customer experiences and maintain an edge in a constantly shifting marketplace.
Implementing and Setting Up Your POS System
Once you’ve selected the ideal Point-of-Sale (POS) system for your business, the next crucial step should be implementing and setting it up correctly. Proper implementation ensures that it integrates smoothly into business operations while providing maximum benefits; this section covers key steps involved with setting up and installing a POS system – preparation, installation, configuration and staff training are just some examples of this.
1. Preparing for Implementation
Overview:
Preparation is key to the successful deployment of any point-of-sale system, helping avoid common pitfalls and guaranteeing that it meets your business needs from day one.
Preparation Steps:
- Evaluate Existing Systems: Assess your current processes and systems to identify those which will be integrated or replaced by the new POS system.
- Define Objectives:Set out what your objectives for the new POS system are – improving inventory management, providing superior customer service or streamlining payment processing are among them.
- Gather Requirements: Take stock of the needs for your business by listing out specific hardware, software and integration requirements.
- Prepare Your Team: Be sure to inform and prepare your staff for upcoming changes, explaining how the new system can benefit their daily tasks.
Checklist for Preparation:
- Review current systems and processes
- Set objectives and goals
- Gather hardware and software requirements
- Prepare staff for system changes
Example: Retail stores transitioning from manual cash registers to modern POS systems should evaluate current inventory management practices, establish goals such as improved stock tracking and brief their staff on what features and benefits the new POS offers.
2. Installing the POS System
Overview:
Whilst setting up your POS system requires both physical and software components to function seamlessly together, installation is also an integral step in making sure everything functions as planned and efficiently.
Installation Steps:
- Hardware Setup: Connect all necessary devices such as POS terminals, barcode scanners, receipt printers and card readers together before verifying all are functioning as expected. Ensure all are properly powered up before proceeding further with setup.
- Software Installation: Once the POS software is on a system, its installation may include configuring settings, integrating with other software and importing data. Network Configuration: Initiate network connections that include Internet access as well as any local configurations required for system functioning.
- Software Installation: Install the POS software on the system. This may involve configuring settings, integrating with other software, and importing data.
- Testing: Make sure all hardware and software components are working as intended by performing tests of transactions, inventory management, report generation and report verification to verify functionality.
Table: Common POS Hardware Components
| Hardware Component | Purpose |
|---|---|
| POS Terminal | Central unit for processing transactions |
| Barcode Scanner | Scans product barcodes for sales and inventory |
| Receipt Printer | Prints transaction receipts for customers |
| Card Reader | Processes card payments and electronic transactions |
Example: Installation of a point-of-sale (POS) system at a restaurant entails setting up terminals at each table, connecting kitchen printers for order tickets, and configuring software to manage menu items and table management.
3. Configuring the POS System
Overview:
When it comes to configuring your point-of-sale system settings, customizing them according to your business processes and preferences is key to making sure the system runs efficiently while meeting all of your individual requirements.
Configuration Steps:
- Customize Settings: Tailor system settings to match your business requirements, such as tax rates, payment methods and receipt formats.
- Import Data: Import existing inventory lists, customer information and sales histories into the new system.
- Set Up User Accounts: Create and configure staff member user accounts with appropriate permissions and access levels.
- Integrate with Other Systems: If applicable, integrate the POS system with other business systems, such as accounting software, inventory management tools, or e-commerce platforms.
Table: Key Configuration Tasks
| Configuration Task | Description |
|---|---|
| Customize Settings | Adjust tax rates, payment methods, and receipt formats |
| Import Data | Transfer existing data into the new system |
| Set Up User Accounts | Create and configure staff accounts and permissions |
| Integrate Systems | Connect with accounting, inventory, and e-commerce systems |
Example: Retail stores may configure the POS system with multiple tax rates based on product categories, import inventory data from an Excel spreadsheet and integrate with accounting software for seamless financial reporting.
4. Training Your Staff
Overview:
Training is key to ensure that your staff can effectively use a new POS system, with minimal disruptions and to help employees acclimate to its use. Proper instruction helps reduce disruptions while helping adapt staff members to adapt to its use.
Training Steps:
- Deliver Comprehensive POS System Instructions: Deliver training sessions that cover every aspect of using a POS system – daily operations, troubleshooting and reporting are just some of the issues addressed during these training sessions.
- Create User Guides: Create user guides and manuals to serve as resources for staff to refer back to as necessary. Include step-by-step instructions for common tasks and troubleshooting tips in these documents.
- Deliver Ongoing Support and Resources: Make sure staff have access to ongoing resources and support if any questions or issues arise following initial training.
- Gather Feedback: Solicit staff feedback about the training process and usability of the POS system, and use this input to make improvements and address any concerns that may have arisen.
Checklist for Staff Training:
- Conduct comprehensive training sessions
- Provide user guides and manuals
- Offer ongoing support and resources
- Collect and address staff feedback
Example: In a fast-food restaurant, staff training would include instruction on using the POS system for quick order entry, handling special requests, and managing cash and card payments efficiently.
Conclusion
Implementation and setup of a point of sale (POS) system require careful preparation, careful installation, precise configuration and effective staff training. By adhering to these steps you can ensure a seamless transition into your new POS system, maximize its benefits and strengthen business operations.
Investment in an appropriate POS terminal not only streamlines transaction processing but also increases inventory management, customer relationship management and overall business efficiency. As technology develops further, small businesses can stay competitive by selecting a system which aligns with their growth and operational goals – with confidence they can navigate payment processing complexities while offering outstanding service to their customers.